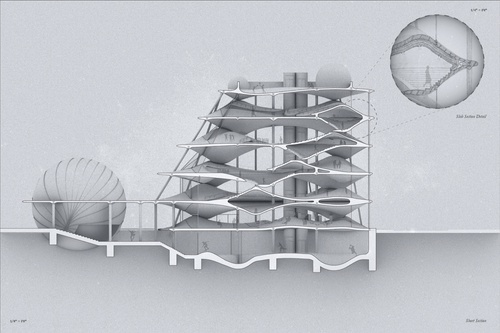
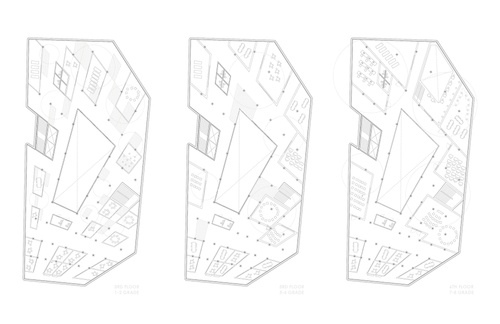
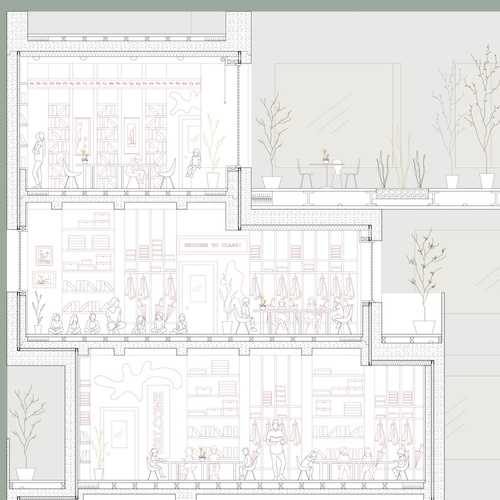
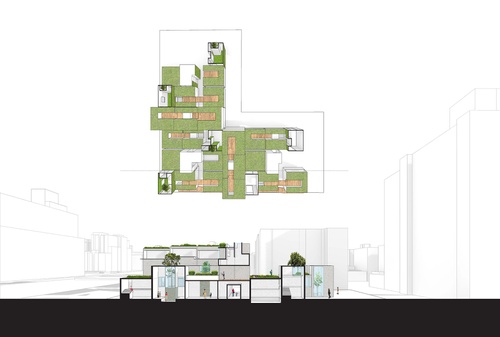
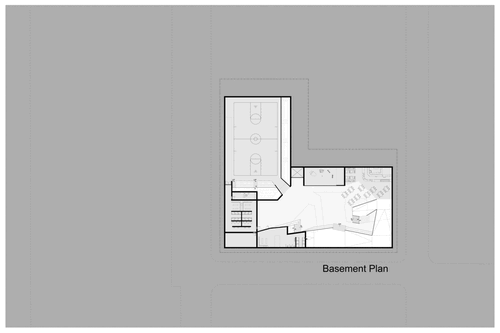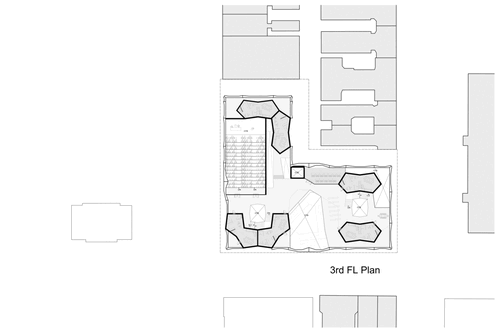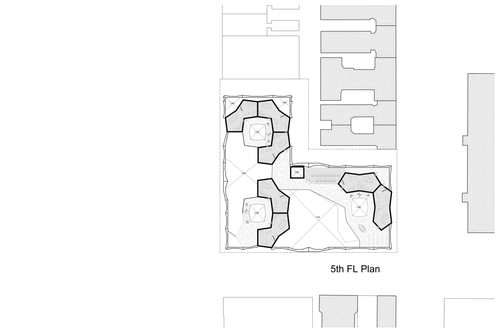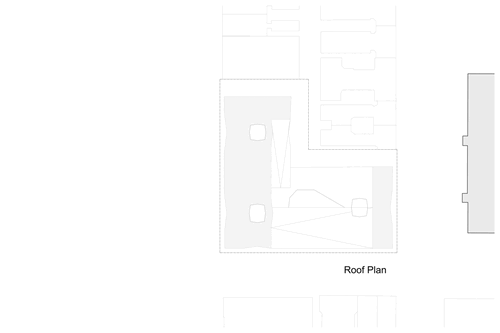
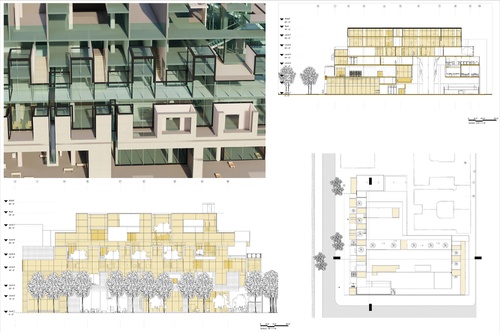
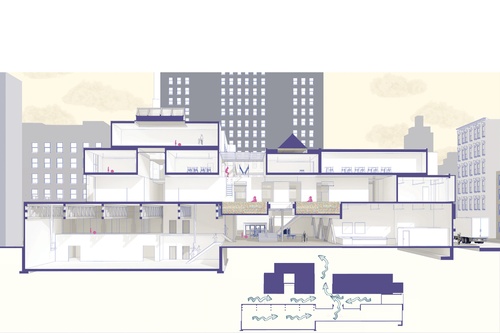
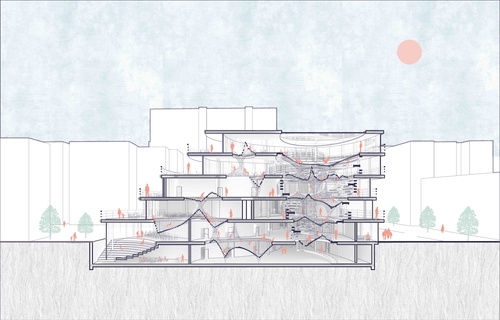
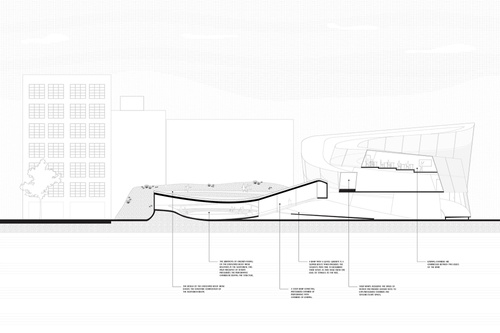
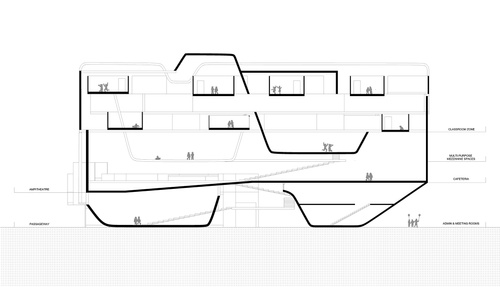
Introduction
Core Architecture Studio II
Environment as the Third Teacher
A school is more than just its students, teachers, and textbooks; it also includes a building, which is essential to a child’s education and personal growth. Loris Malaguzzi, founder of the Reggio-Emilia educational philosophy in the early twentieth century, called the environment the “third teacher,” together with a student’s parents and teachers. In its full manifestation, the multidimensional school environment inspires and nurtures children by activating all of their senses—a position that Core Architecture Studio II explored this semester.
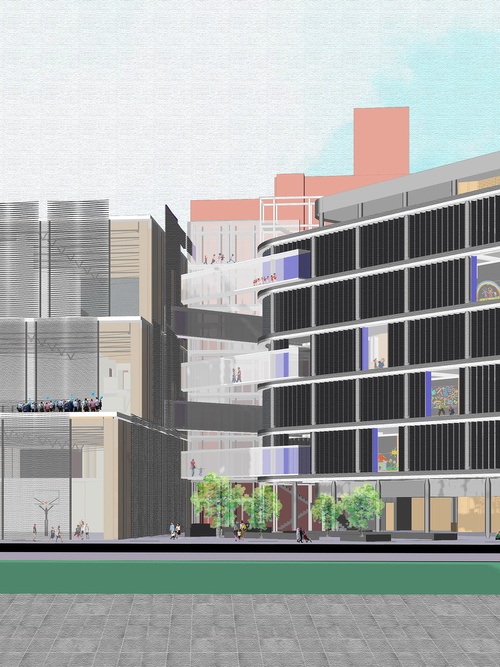
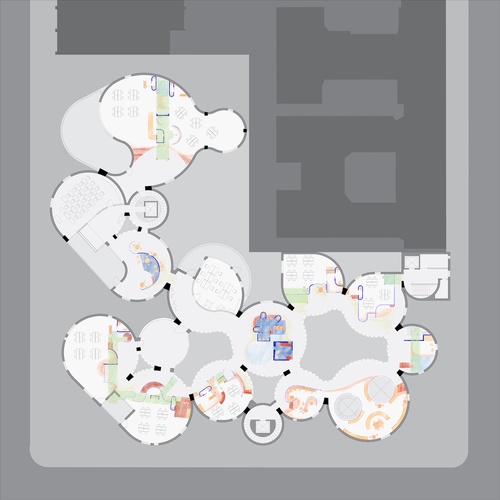
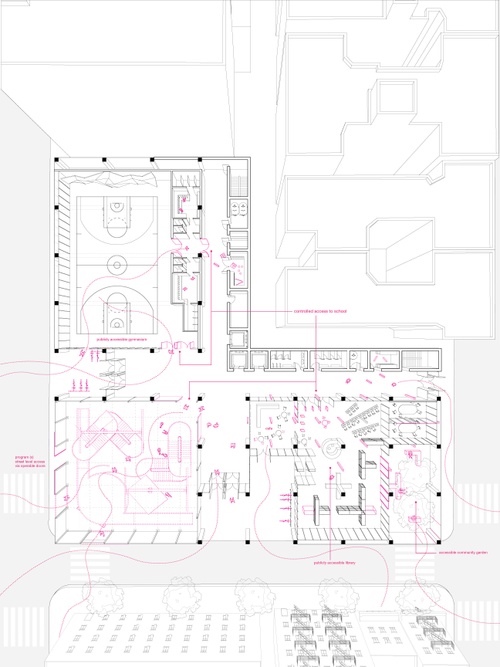
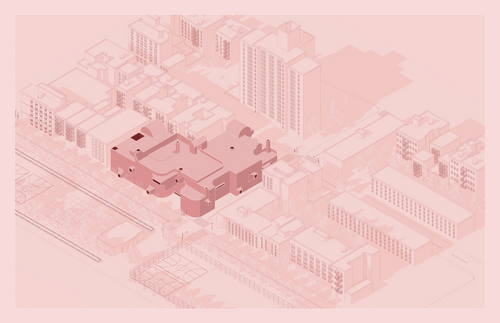
All eight Core II studios focused on the design of a K-8 public school on the site of P.S. 64, located on the Lower East Side of Manhattan. Designed by C.B.J. Snyder in 1906, P.S. 64 served as a New York City public school for seventy years before it was shuttered. Today, the building remains abandoned. As part of the research for their design projects, Core II students visited the vacant building, studied its history, and evaluated its current condition in order to envision ways to revitalize the site as a contemporary school.
How can a building both react to and affect pedagogy? When a child feels safe and supported, they will take risks and embrace challenges. How do we design spaces that nurture and inspire individual children so they can reach their fullest potential? At the same time, how does a school, as a civic institution, connect to its community and promote fruitful interactions between the students and the community? How do our schools reflect our cultural values and prepare children for their own futures (not just our present)? How do we build a school today that will serve not only this generation of children, but also the next?
Through many scales of engagement—from the site in general to the detail of a brick—students devised careful interventions in the existing structure. An essential aspect of the curriculum prompted students to emphasize low-embodied carbon structural design. In response, projects reused the existing building or elements of it, integrating new materials with low-embodied carbon footprints and thoroughly considering the future use and lifespan of the structure.
1
Kinetic Intelligence
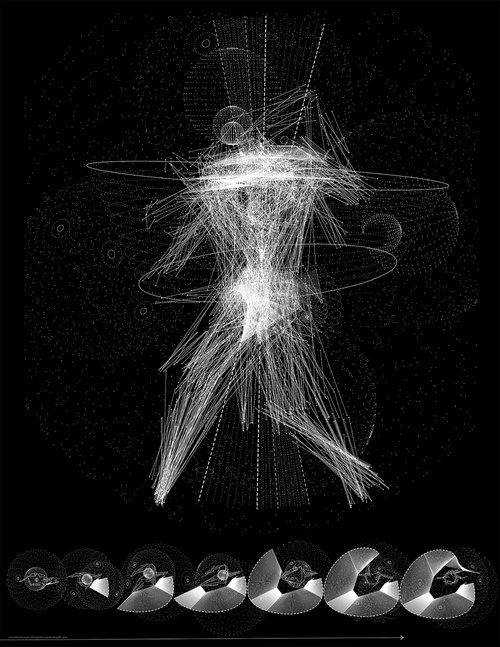
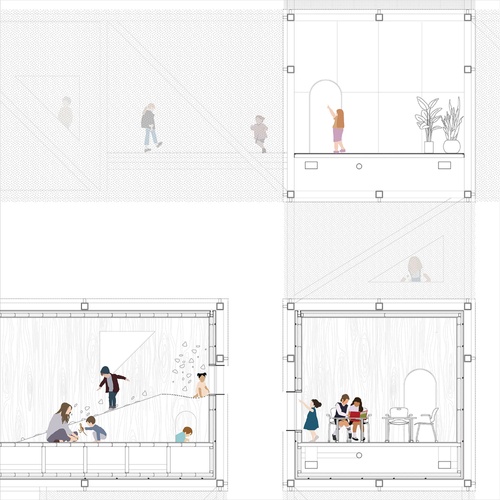
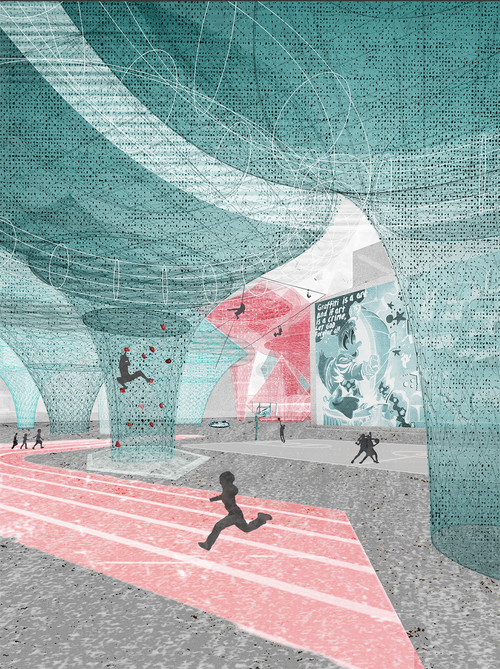
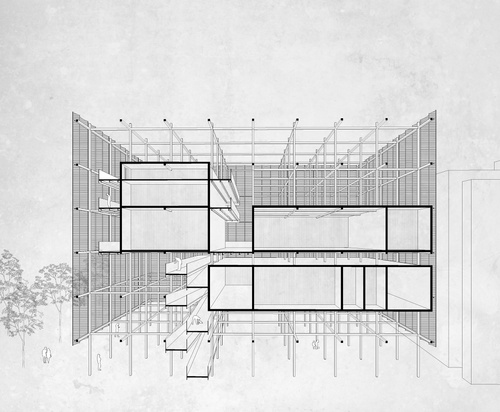
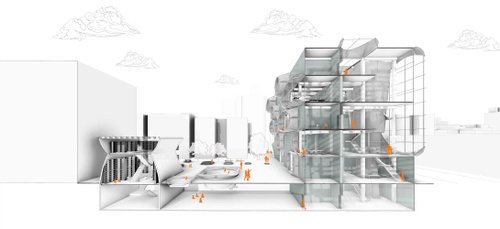
As a foil to Artificial Intelligence, a term this studio referred to as Kinetic Intelligence recognizes the correlation of the body to the mind in the context of learning, as is supported by keen research identifying a sophisticated intelligence of the body in motion as it moves through space and time. In the development of a school proposal, studio participants explored spatial logics in accordance with the realm of the body. They delved into the space of learning, speculating critically between conducive postures, spatial configurations, and sensory stimulation that use existing data to reimagine an optimal learning environment. Students were challenged to express program organization speculating critically and imaginatively around where does the school begin and where does it end, if at all.
ARTIMEDU - School of Arts and Craft
ARTIMEDU is a school of arts and crafts open to all students interested in arts, from kinderga...
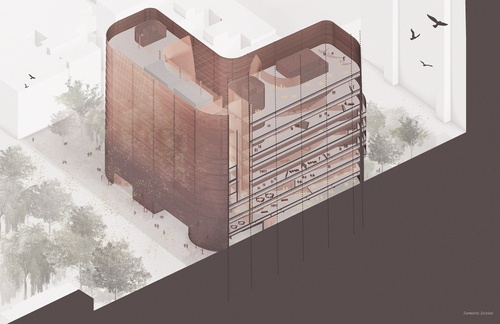
Breathe . Diffuse . Dissipate
The new K-8 school is imagined as a membrane that acts as a ventilated buffer between the city...
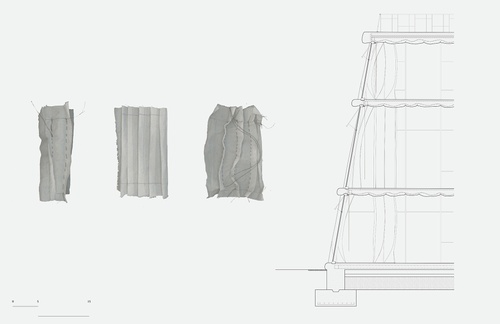
carrying project
This project begins by looking at the body performing the mundane act of carrying a bag. In on...
2
All is School
Learning is not limited to the young, nor is it confined to a given place or a given time. Learning happens everywhere.
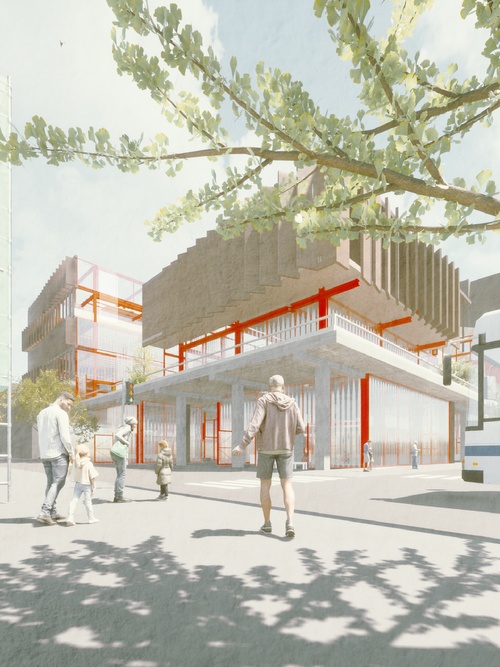
As institutions well integrated into the fabric of the city, schools have the potential to evolve from isolated educational silos into broader cultural platforms active in the public realm. This studio sets out to re-imagine schools as an open-ended, multivalent civic infrastructure for learning that sits at the center of contemporary urban life – spaces able to participate more actively in urban life while welcoming communities to become more engaged with school life.
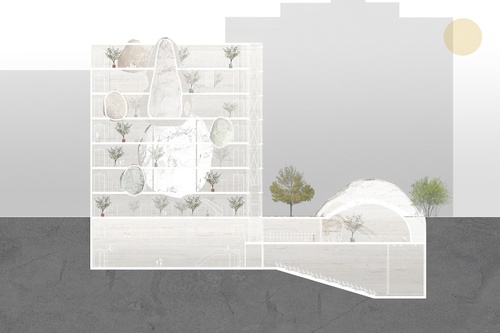
Grounded Exploration
What freedoms can the school afford that the city does not? From the perspective of a child, N...
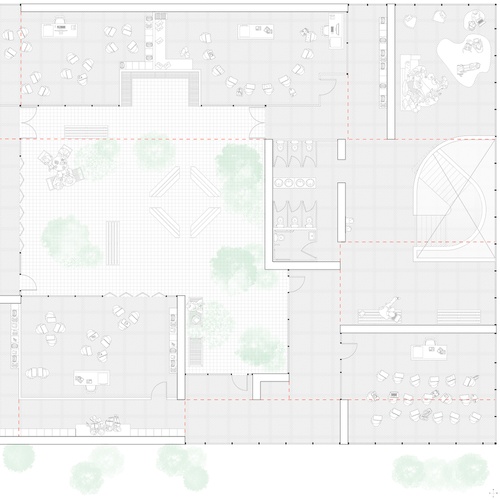
Solace School
Inspired by the immediately adjacent Sarah D. Roosevelt Park, this project is designed as a se...
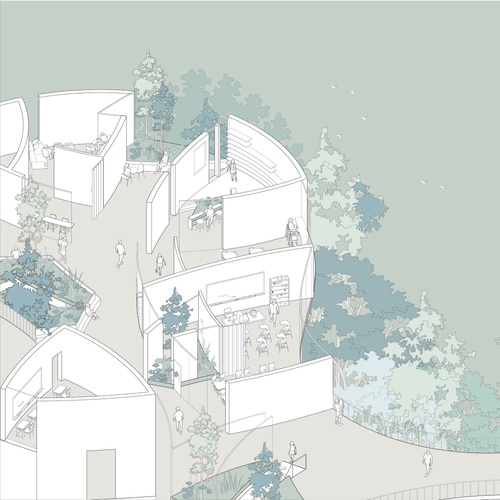
Inside Out
Sara D. Roosevelt Park is a significant public space with dense foliage and traces of diverse ...
3
Open Frameworks
This studio resonates with Cedric Price’s belief in “architecture’s potential to nurture change, intellectual growth, and social development rather than to offer a definitive aesthetic statement.” It took on this attitude, proposing architectural artifacts that are open-ended and flexible even if proposing specific material arrangements. In shifting perspectives from “Object to Performance” projects focused on architectural behaviors, addressing pressing climatic, political, spatial, and social contemporary challenges. Students paid particular attention to the political agency of schools, as they relate to our everyday communities while addressing the agency of the collective to define school curriculums. They explored the potential of the hybridization between the classroom and surrounding cultural environment, in other words, between school and the city.
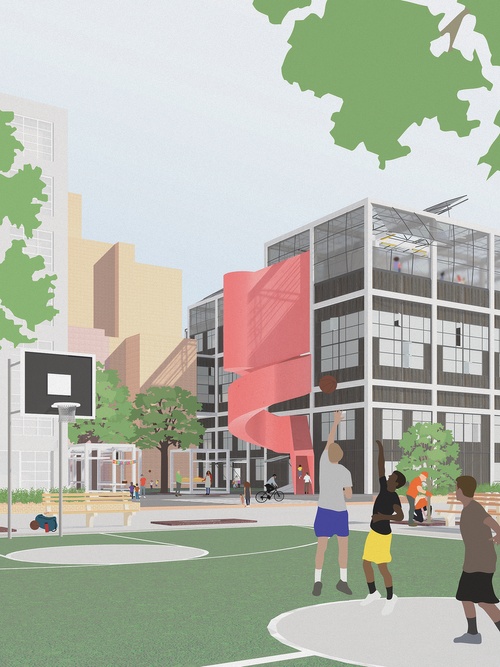

School-Public
Who is a public school for, or perhaps, when is it for?
New York City’s high rates of ch...
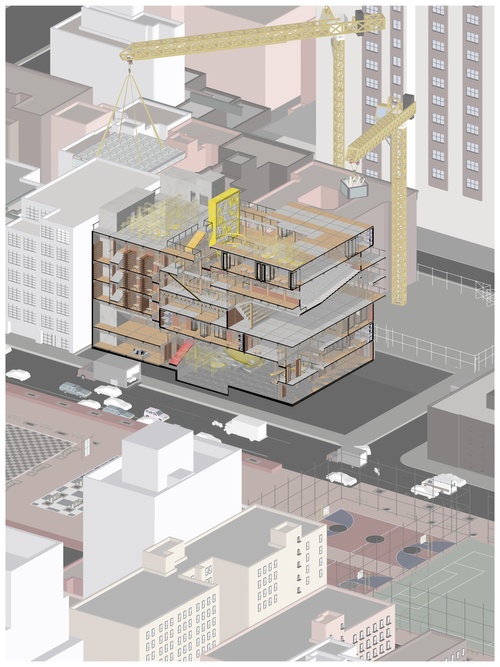
Playtrium
The following school proposes to conditionally invite the public to engage with its students w...
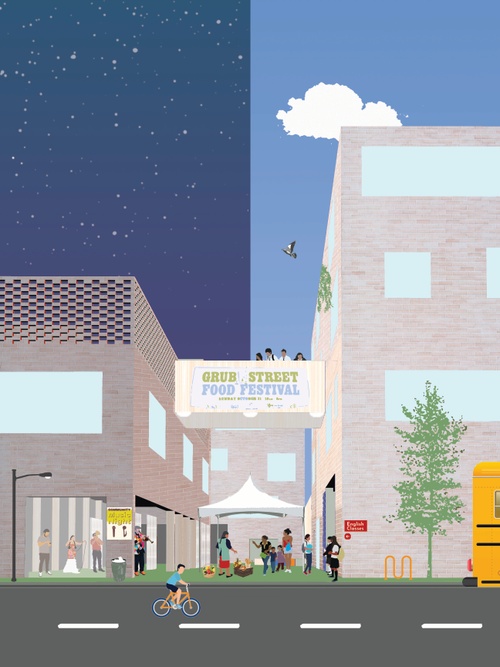

LES Alley School
A subversion of unused alleyways commonly found in the Lower East Side, this school proposes t...
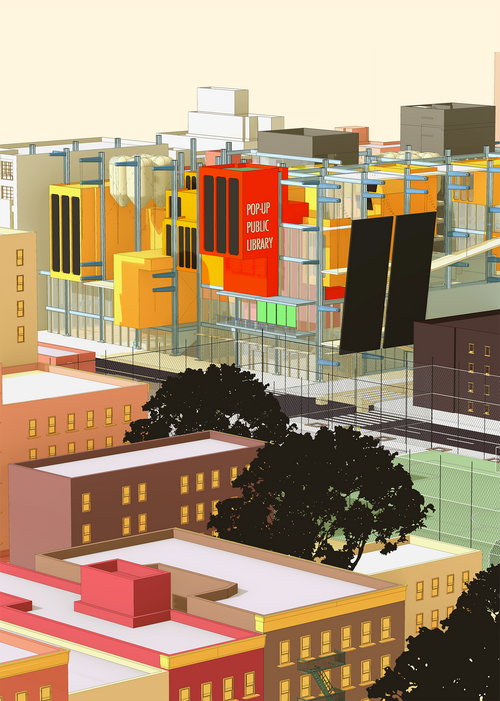

The Plug-in School
The Plug-in School starts inside-out as the core becomes the facade and an urban membrane wher...
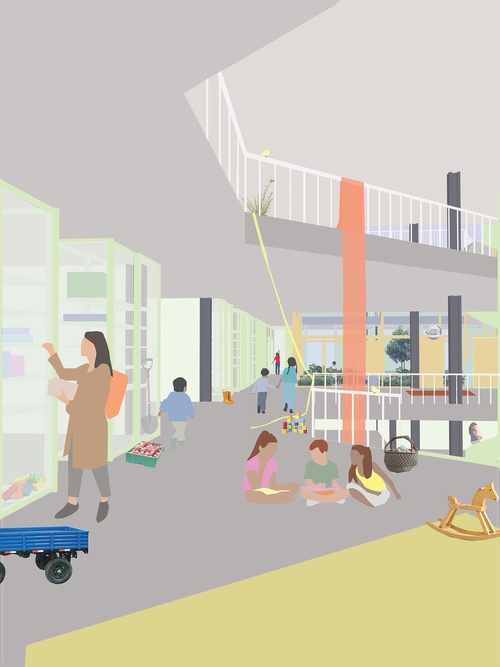

School for Exchange
The school, as a civic center, should offer no bounds to the possibilities of a growing commun...
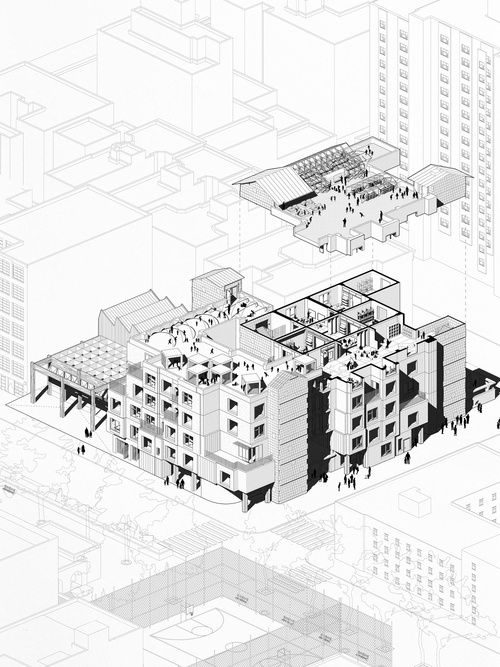
Storefront Interactions: A School for Contextual Learning
Storefront Interactions is a K-8 public school that seeks to provide a contextual learning env...
4
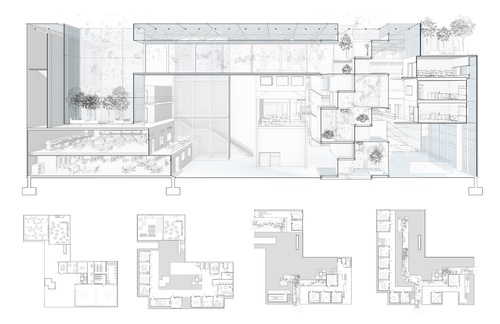
Post Carbon School
This studio operated from a basis of energy and resource scarcity by doing as much as possible with as little as possible. Rather than an approach characterized by austerity, however, students rethought school building from the ground up by questioning basic assumptions that undergird the carbon economy. The site exists in the world’s wealthiest city, but students attempted to operate with the resourcefulness, efficiencies, flexibilities, and informal systems seen in parts of Asia, Africa, and South America as precedents for design and construction. Could these methods from the global South help us to reimagine ways a school functions both locally and by extension globally? How could the implementation of such strategies define new territories for the school and its site?
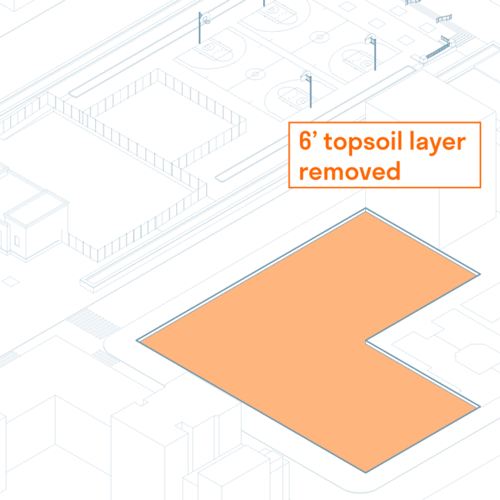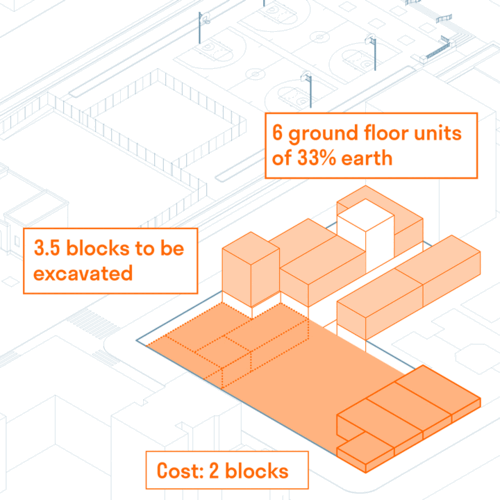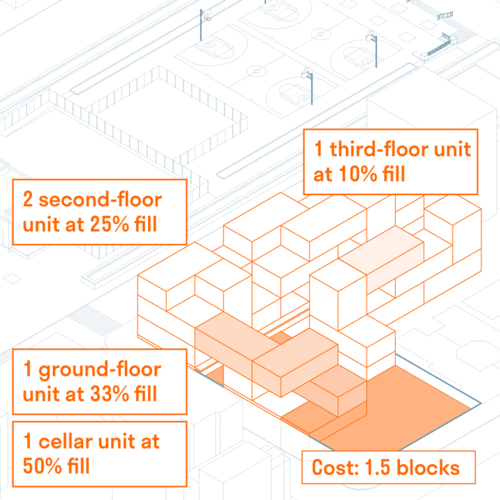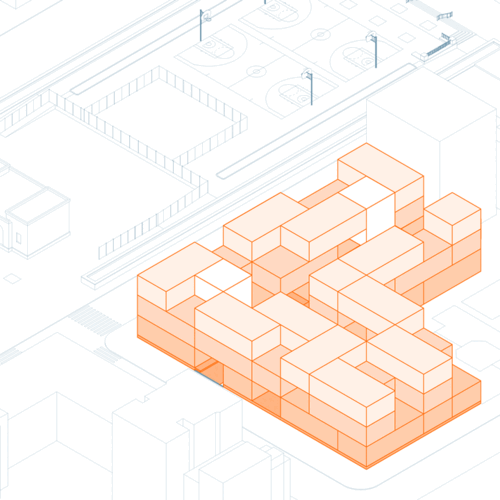
Strata School
Strata School is a K-8 public school that teaches students how to live justly in the Anthropoc...
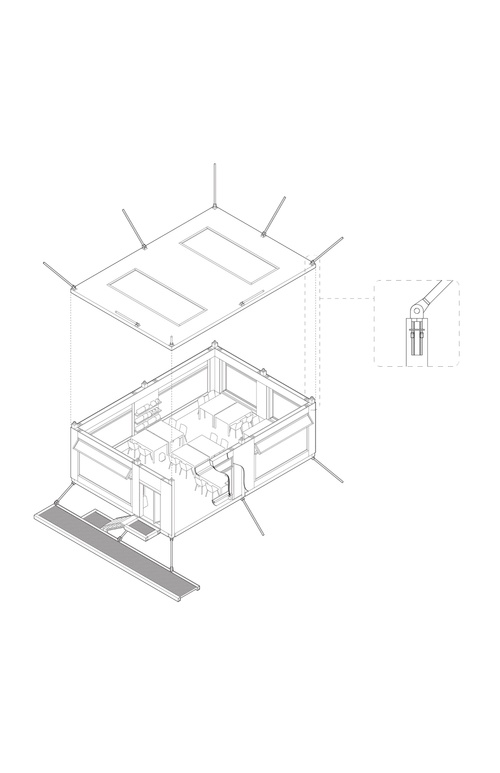
The School of Amalgamation
The school of “Amalgamation” focuses on a curriculum of substance circular economy and fosters...
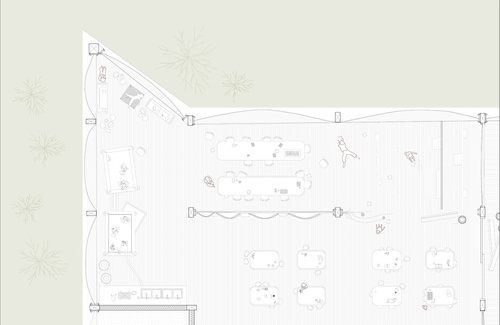
Paper, School
This project reimagines the school as a stack of paper: an imagination of post-carbon educatio...
5
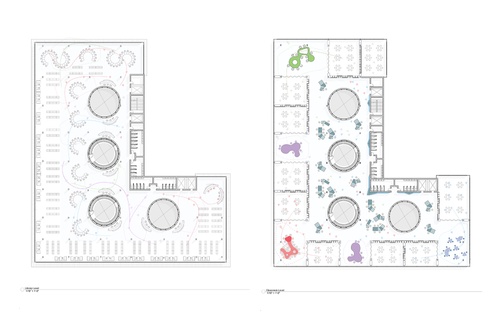
Focused Thought: Kinesthetic Awareness
The proposition for the studio was founded upon a kinesthetic education that explores the fundamentals of education through the invention of study models and the logistics of the program requirements. These learning machines examined local parts to define the mass of the school as a whole. In tandem, students studied various educational methods along with the core values of the community as a counterpoint for the development of its constituents, how agency is established through a sense of self-awareness in relation to others as it assists social interaction and autodidactic life is the goal of this enterprise. Other critical issues addressed were remote learning, materiality and matter, access to natural light, and the notion of ethically equitable education.
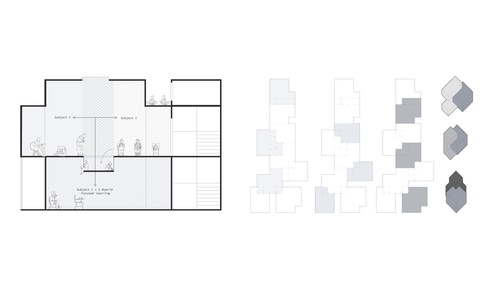
The Discovery School
Public education is a great privilege. However, the standard education system in our country h...
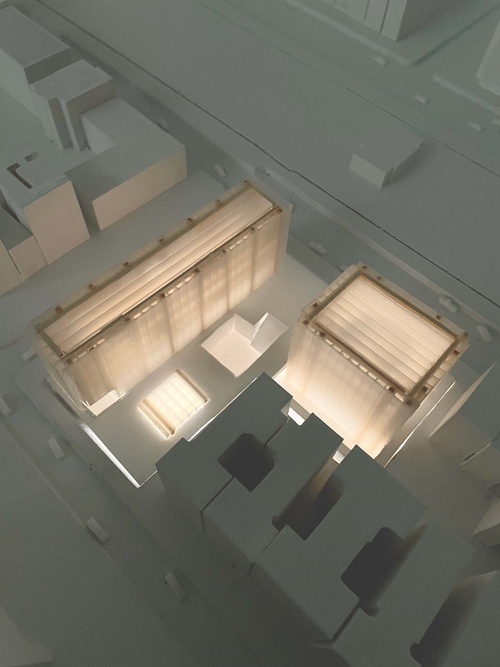

Reframing the Alley
Childhood education is a process: one that requires the promotion of curiosity, independence, ...
6
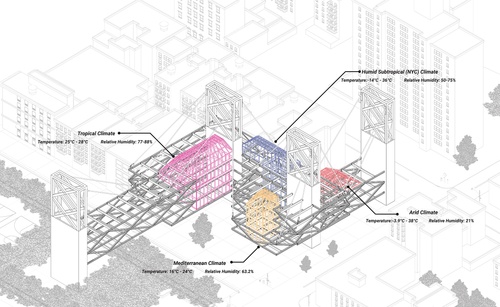
Transmittance
While schools require electric light to serve their communities, this studio embraced daylighting design as an impetus for architectural invention. Students sited and sculpted buildings to strategically respond to daylight. They designed facades that transmit, absorb, and reflect the sun’s light. They worked with materials to shape our building interiors so that light and shadow can syncopate with our circadian rhythms. They considered how natural light, together with its shadow, can inspire a path of self-enlightenment no matter how it’s defined.
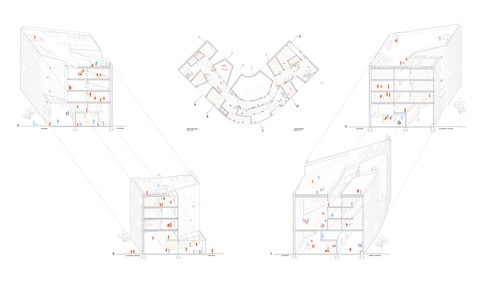
The Overlook School
The Overlook School reimagines a thriving educational environment for the Lower East Side&rsqu...
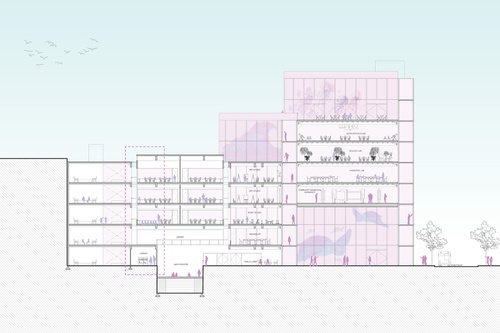
Forsyth Art School
Forsyth Art School integrates art-making in the curriculum not only at the classroom level but...
7
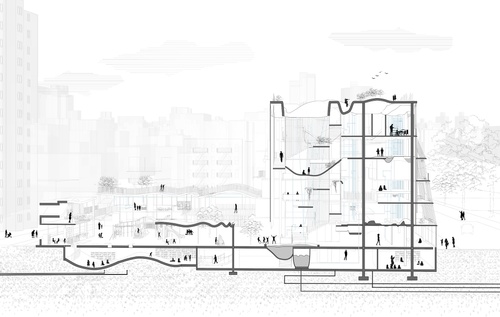
Entangled Bodies
At a moment when democracy, the climate, and truths are in simultaneous and divisive crises, perhaps nothing is more important than education. Students’ intense passions, beliefs, and curiosity were channeled to guide the narratives and trajectories of their projects, uncovering futures we can impact but not fully predict. Spaces of learning have the utmost opportunity and responsibility to inspire and enlighten. Buildings are understood through material and spatial agency encompassing nuanced gradients of hard-, soft- and weather-scapes, intertwined to support education, community, and regenerative legacy. Architecture and gardens are interdependent and associative, creating healthy and resilient experiences shifting through the changes of seasons, and interacting with sunlight and moon-shadow.

Transient Thresholds : Liminal Voids
Education is a transitory period in one’s lifetime, where a K-8 school occupies nine years of ...

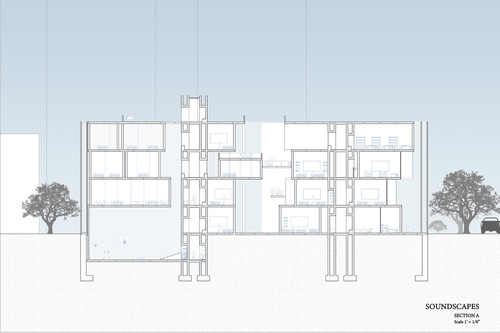
Soundscape
Classroom acoustics can drastically affect the well-being of students in early education. Mari...

Over the Bend & Across the Archipelago
There’s a thin line between fear and growth, and a gradient between chaos and calm. Abrupt cha...
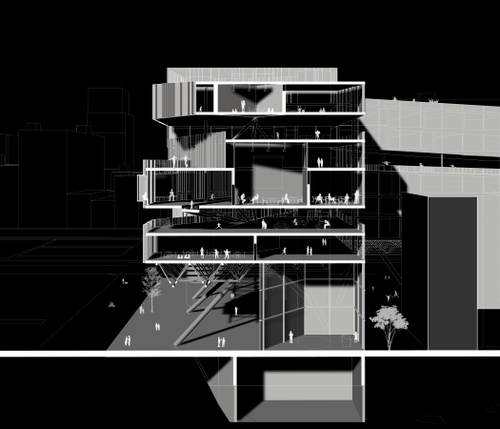
Confluences in Transit
How can the intermingling of people be advocated through the design of a school? Formal learni...

No Service: Joint, Grid, Pleat
Layers of threshold spaces situate within a grid system. The lightness of the elements is regi...
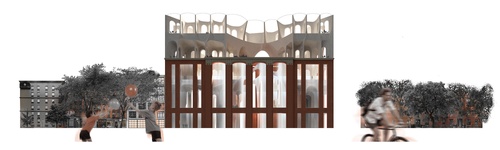
Soft Formworks
Public education has focused on implementing benchmarks and standardized testing in order to a...
8
Learning Environment
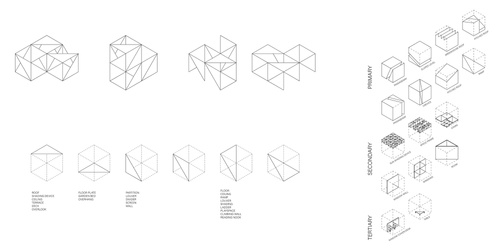
Architects and designers of the built environment now navigate a crisis stack of existential impacts on the world around us. The term ‘environment’ is ubiquitous and so broadly used that it has all but lost its meaning. This studio took education innovator Loris Malaguzzi’s insight that the environment is the third teacher as an entry point for the design of a grades K-8 public school on New York City’s Lower East Side. It asked: What exactly is the environment? What is its relationship to learning? And how do we harness architecture’s capacities to drive behavior?
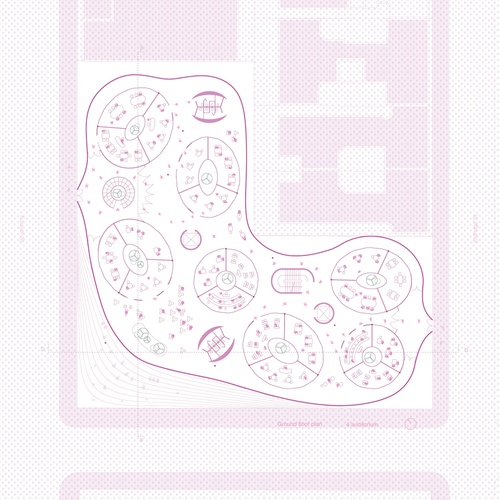
The Porotic School
The Porotic School exposes students to the unique constructed natural environment in the city....
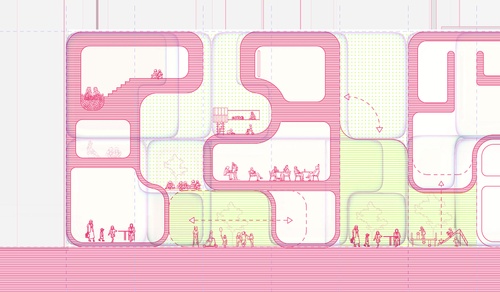
Respiring Thresholds
This Children’s school is derived from the pneumatic system of the physical act of breat...