Our food system is largely centralized and it’s failing. The agricultural industry is becoming more monopolized every day, while the average meal in the US travels about 1,500 miles, where 40% of the nutrition is lost, and 1/3 of the food goes to waste. In California, wildfires and the Covid-19 pandemic caused supply chain problems affecting centralized food production. These factors caused a drastic increase in the food insecurity rates of Los Angeles in 2020. Demographics of LA show that obesity and income are directly related. When income decreases it prevents access to healthy food, leading to an increase in obesity.
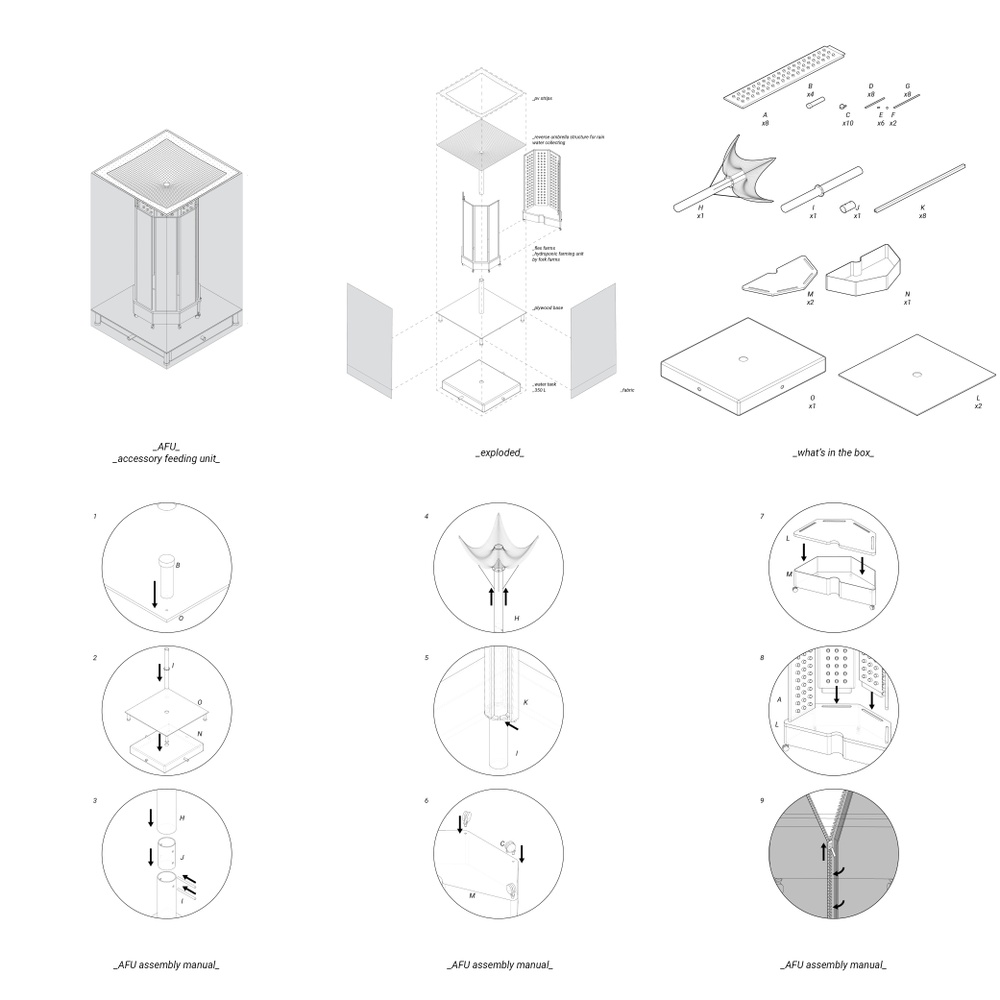
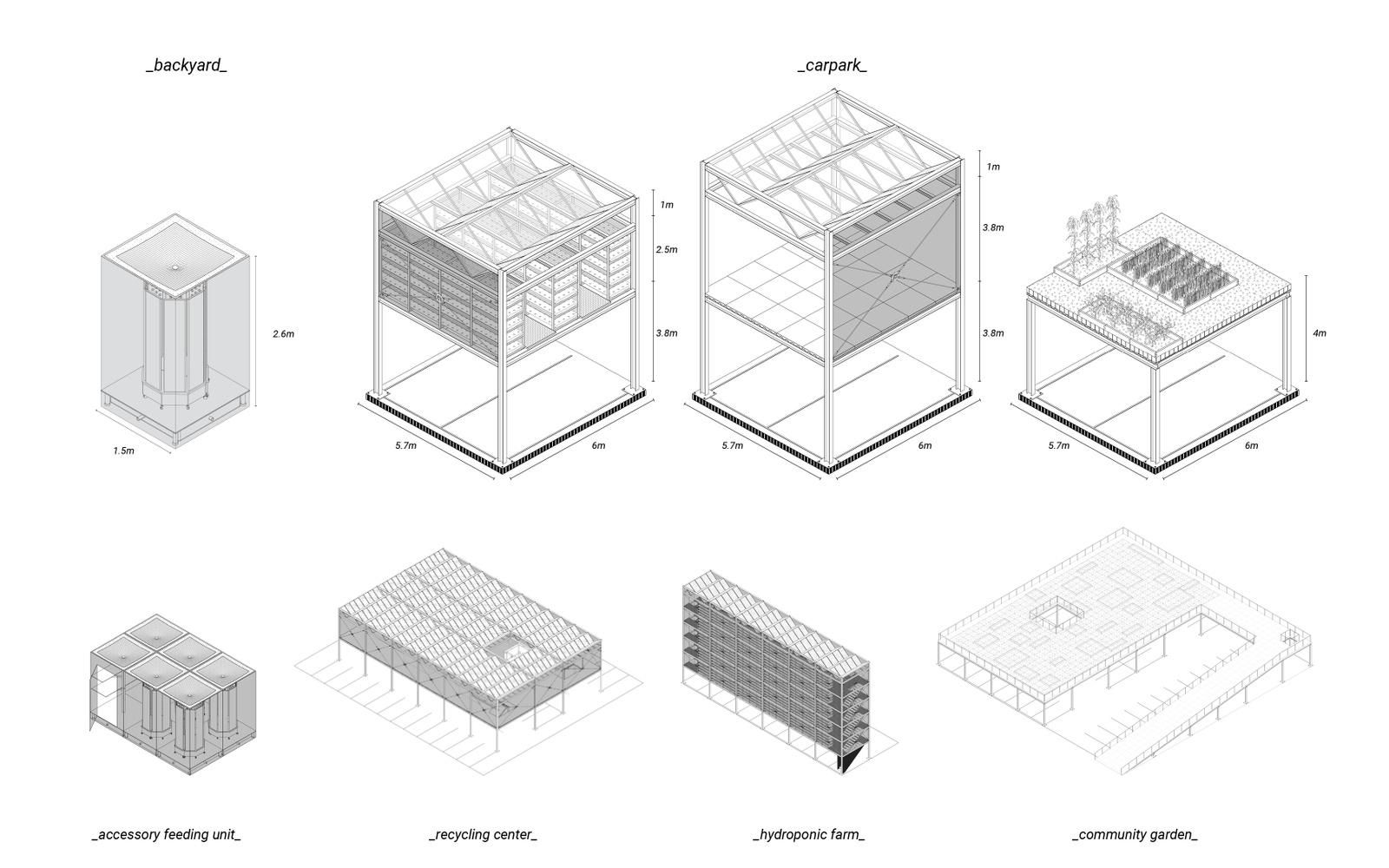
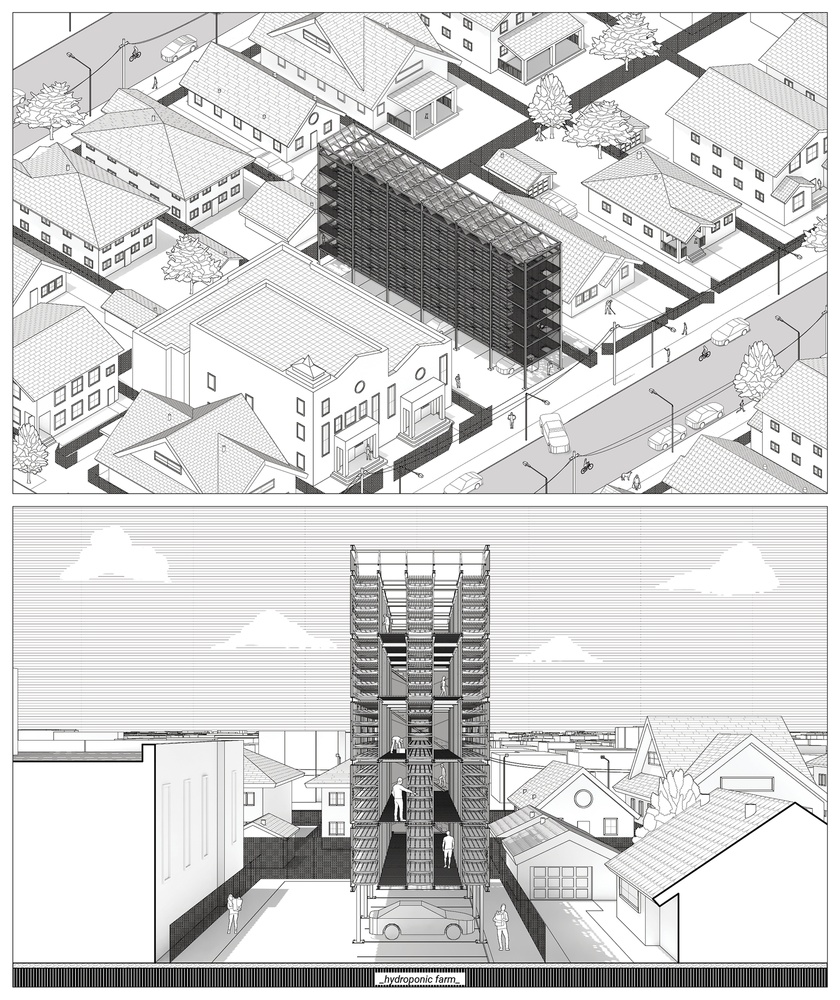
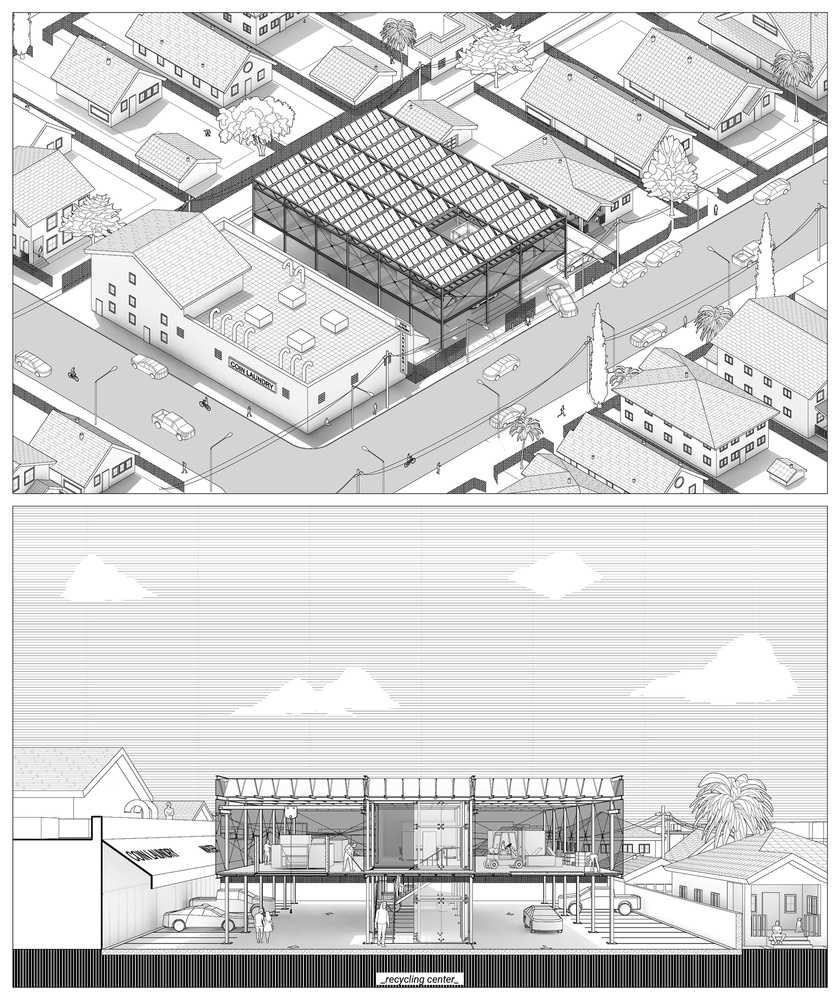
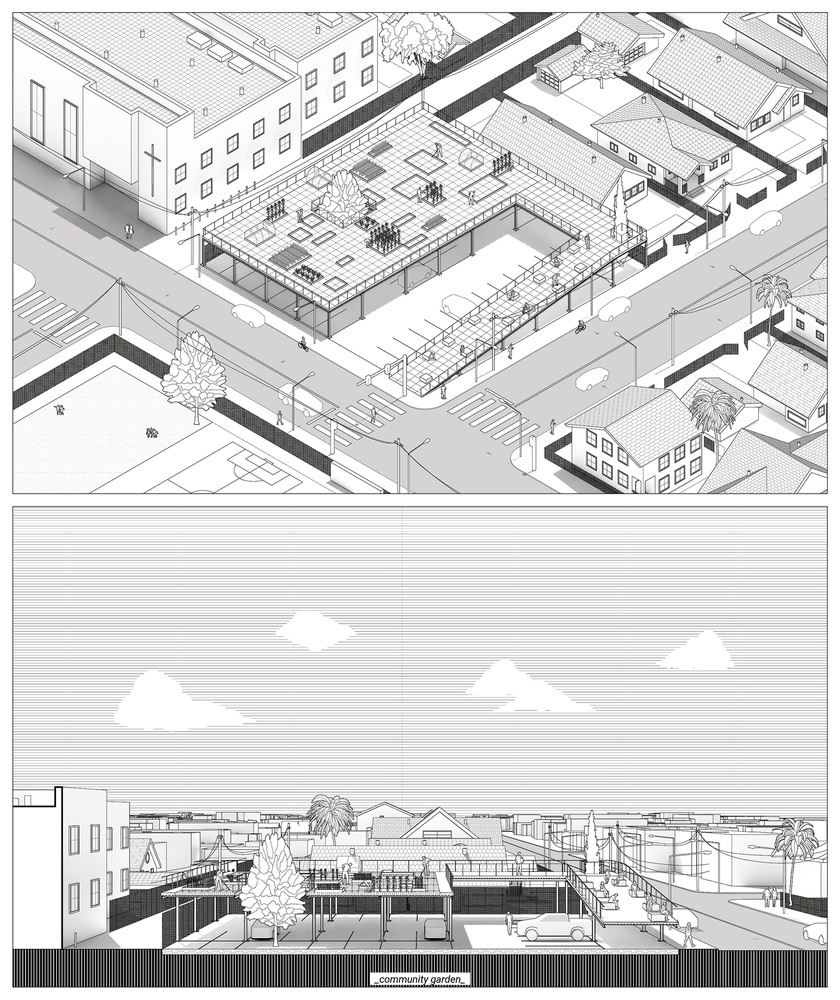
The project proposes a decentralized food system in LA to decrease food insecurity and provide fresh produce to underdeveloped neighborhoods. Central Alameda is chosen as a case study site, where the income to obesity rate is extreme. In this regard, the project offers solutions on two different scales. The first one is accessory feeding units for backyards as a replacement for accessory dwelling units. It’s a modular hydroponic unit for people to produce their own fresh produce in their backyards. The second scale is attached to the car parks, elevated modular structures with three different programs: hydroponic farms, recycling centers, and community gardens. Hydroponic farms will provide fresh produce to people with no backyards, schools, and industrial areas. Recycling centers will recycle plastic bottles to manufacture parts for other facilities. Lastly, community gardens offer a gathering space and a ground for agricultural education.